Light Waves
- Light is an electromagnetic wave with electric and magnetic fields propagating at speed: where:
- Wave equations: with and and being perpendicular. You will learn more about this in Introductory Electromagnetic Theory
Light Intensity
- Definition:
- Electromagnetic wave intensity:
- Interference of two equal beams with phase difference ( \Delta \phi ):
Michelson Interferometer
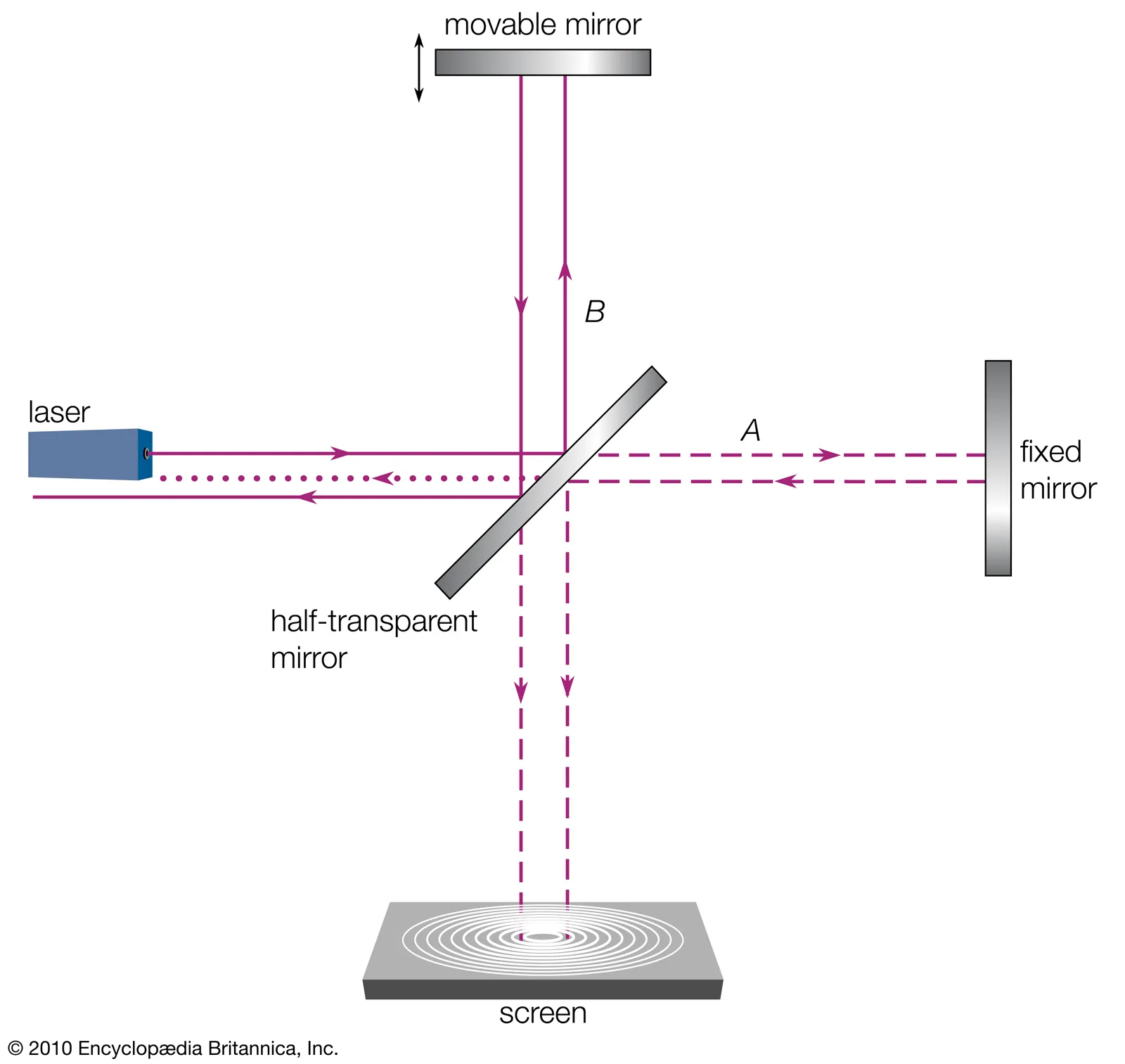
- Intensity split at mirrors:
- Final intensity at detector:
- Phase difference:
LIGO Interferometer
- A large-scale Michelson interferometer used to detect gravitational waves.
Young’s Double-Slit Experiment
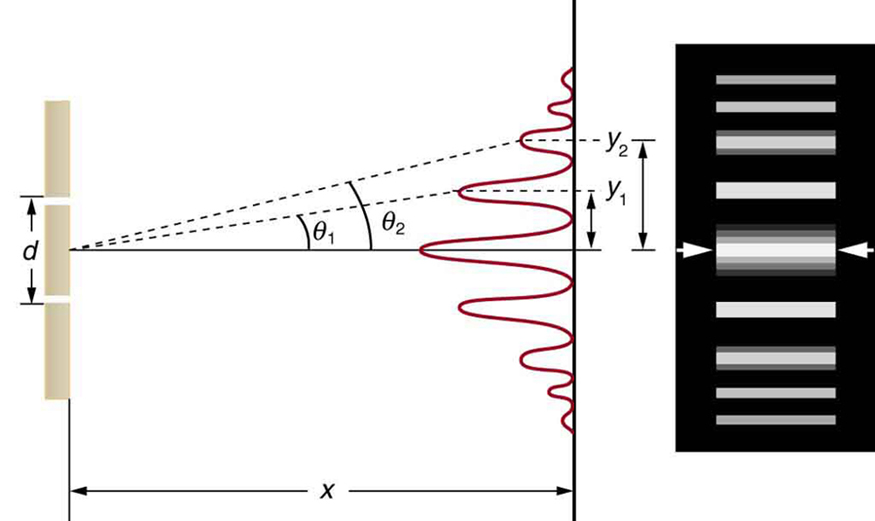
- Light passes through two slits and interferes on a screen.
- Path difference determines phase difference and interference pattern.
Two-Slit Interference: Arithmetic
- Constructive interference:
- Destructive interference:
- Phase difference:
Light: Wave or Particle?
- Light is unique because:
- It is the fastest carrier of information.
- It consists of massless particles carrying energy and momentum.
- It interacts directly with our senses.
- It has wave-like and particle-like properties.
Interference and Diffraction Effects
- Examples:
- Soap bubble colors
- Opalescence (e.g., opals)
- Butterfly wing coloration
- Laser speckle patterns
- Halo around the sun or moon
- Applications:
- Holography
- Film thickness measurement
- High-precision spectroscopy
Thin Film Interference
- Interference from reflections in thin films causes color patterns.
- Observed as fringes when using monochromatic light.
- Observed as color bands with white light.
The Photoelectric Effect
-
Observation:
- Light ejects electrons from a metal surface.
- The energy of ejected electrons depends on light frequency, not intensity.
- No measurable time delay for electron ejection.
-
Photoelectric equation:
where:
- ( h ) is Planck’s constant (( 6.626 \times 10^{-34} ) J·s),
- ( f ) is the frequency of light,
- ( \Phi ) is the work function of the material.
-
Stopping potential:
Einstein’s Photon Hypothesis
- Light consists of quanta or photons.
- Each photon has energy:
- The concept helped explain the photoelectric effect and led to quantum mechanics.