Maxwell Equations
Faraday’s law: an EMF is produced around a loop when magnetic flux passing through the loop changes. This is how inductors work.
RHS of Faraday’s law
LHS of Faraday’s law
Faraday’s law
Lenz’s Law: States that the system is always going to be in opposition to change. Formally, the inducted current creates an induced field to oppose the change in Magnetic Flux.
Example: Magnetic Field pointing into page, loop across the field. The induced current would be clockwise. You can use right hand rule to find this.
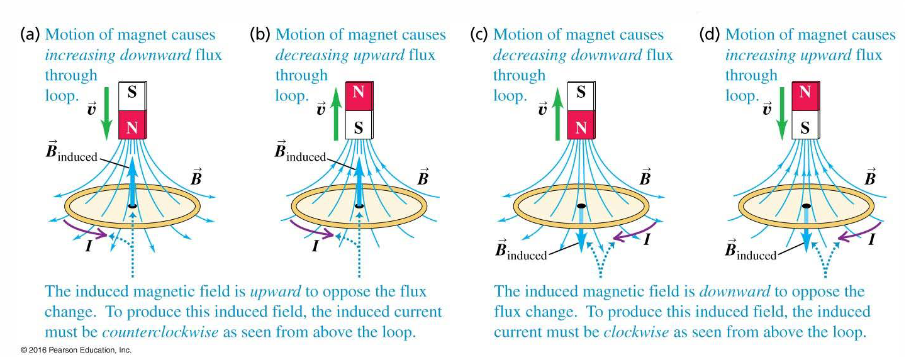 Example of Faraday’s law
Example of Faraday’s law
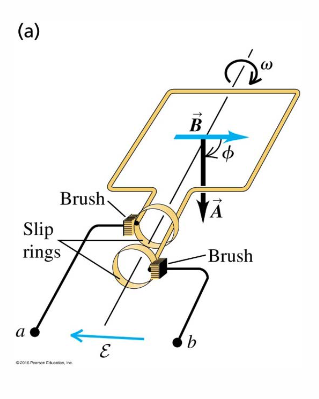
AC generator example
Given Faraday’s law, we have 4 equations to describe the relations between magnetic and electric fields and their sources. We have: Gauss’s law
Faraday’s Law
Gauss’s Law for magnetism
However! there is a problem with Ampere’s Law.
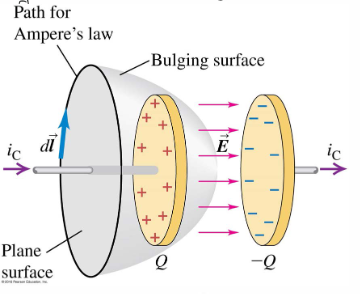
In the above example, the “bulging surface” encloses 0 current, but there is still a magnetic field. Most curious!
Maxwell Solved this by adding a term to Ampere’s Law, called displacement current. Displacement Current is not directly measurable, but is rather induced by a changing magnetic field. In the above parallel plate capacitor example, .
With this displacement current term, amperes law will become
Now, with this addition we have the complete set of Maxwell’s equations.
Gauss’s law
Faraday’s Law
Gauss’s Law for magnetism
Ampere’s Law
What do these tell us?
- Electric field can be generated radially by point charges.
- Magnetic field cannot be generated by mono-poles (don’t exist for this class)
- Electric fields can be generated by changing magnetic fields and vice versa
- Magnetic fields curl around current and vice versa.
- Hence, electromagnetism. Also, learn your right hand rule
Maxwell’s equation + force law will encompass most of EM theory. The only exceptions are more complex matter interaction and material properties.
New Ampere’s law example:
If you have a parallel plate capacitor and want to calculate the magnetic field that is being generated between the capacitor plates, we have no current flowing between the plates but we have an electric field that is changing due to the charge and discharge of the capacitor.
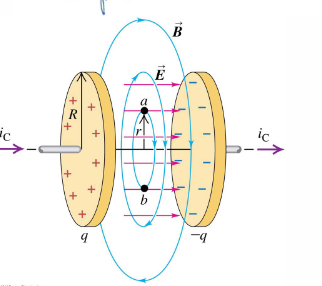
The electric field points from positively charged to negatively charged plate. The magnetic field generated from this will curl around and therefore the circular ampereian loop shown above works for the two plates.
For a circular loop with
Pull B out,
Take derivative wrt time
For r>R