Exponential Analysis of AC circuits
Root mean square
- Square instantaneous current/voltage
- Take the average and square root Given by:
Power in AC circuit
Resistor
capacitors
- As the charge oscillates, energy flows into and then out of a capacitor.
- Ideal capacitors and inductors don’t dissipate any energy.
Inductors
- As current oscillates, energy flows into and out of an inductor.
Complex Exponential analysis
Resistor
Where is the real part. The relation between the voltage across a resistor and the current across is given by Ohm’s Law.
Impedance across a resistor is given by the resistance (what is impedance) In general, the impedance is given by The resistance is in phase and the reactance is out of phase part of current/voltage
$R \to$ "in phase" part of $\frac{v}{i}$
$X\to$ "out of phase" part of $\frac{v}{i}$
Capacitors
Phase change is given by
Inductors
Reactance across an inductor is given by Multiply by = advancing the phase. Multiplying by - delays the phase by .
RC Circuit
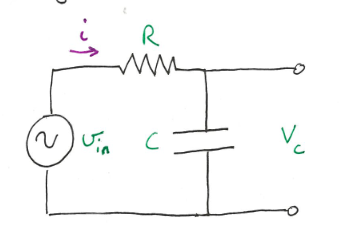
Loop rule:
v_{in} = i\left( \frac{1}{j\omega c} + R \right) $$The [[Impedance]] in the circuit is given by the content in the parentheses abovei(t) = \frac{v_{in}}{R_{t} + \frac{1}{j\omega t}}
\frac{v_{in}\left( R-\frac{1}{j\omega c} \right)}{R^{2}+\left( \frac{1}{\omega} \right)^{2}} \implies v_{in} \frac{R+\frac{j}{\omega c}}{R^{2} + \left( \frac{1}{\omega c} \right)^2}
I = (i \cdot i^*)^{1/2} = v_{in} \frac{1}{\left[ R^{2} + \frac{1}{\omega c} ^{2}\right]^{1/2}}
V_{c} gain = g = | \frac{V_{c}}{V_{in}}| = | \frac{IX_{c}}{V_{in}}|
## RL Circuit ![[Pasted image 20231102110156.png]]V_{in} = V_{0}e^{j\omega t}
v_{in}=[R+j\omega L]
i(t) = \frac{v_{in}}{R+j\omega L} = \frac{v_{in}}{R} \frac{1}{1 + j \frac{\omega L}{R}}
fill this in later... ## RLC Circuit ![[Pasted image 20231102110638.png]]v_{in} = V_{0}e^{j\omega t}
v_{in} = i[Z_{i} + Z_{L} + R] = i\left( \frac{1}{j\omega c} +j\omega L + R \right)
i(t) = \frac{v_{in}}{R+j\left( \omega L-\frac{1}{\omega c} \right)}
v_{out} = Ri = v_{in} \frac{R}{R+j\left( \omega L - \frac{1}{\omega c} \right)}
g_{R} = | \frac{V_{out}}{V_{in}}| = | \frac{1-j\left( \omega \frac{L}{R} - \frac{1}{\omega RC} \right)}{}